Types of Social Dances
Last updated by Mr. Lewis U.U. UttonList of the most popular social dances performed with a partner. These dances often have roots in cultural traditions and can vary widely in style. From ballroom, swing, to Latin.
Waltz
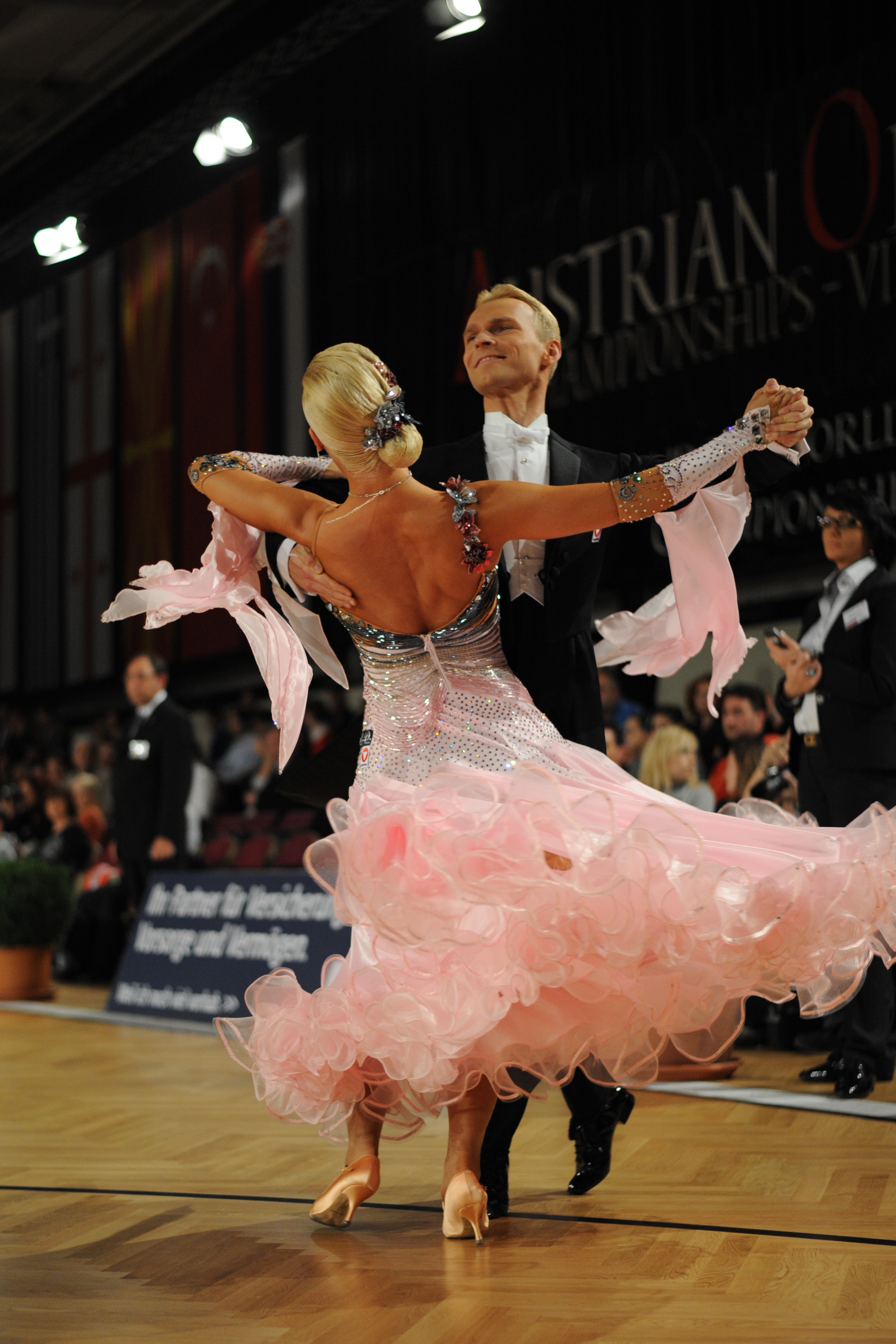 The American Style Waltz is similar to the International Style except the American Style has open dance positions and the dancers legs pass instead of close. The second modification was the “Hesitation Waltz”, which involves taking one step to three beats of the measure.
The American Style Waltz is similar to the International Style except the American Style has open dance positions and the dancers legs pass instead of close. The second modification was the “Hesitation Waltz”, which involves taking one step to three beats of the measure.
Tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries from a combination of Argentine Milonga, Spanish-Cuban Habanera, and Uruguayan Candombe celebrations.
Foxtrot
 The foxtrot is a smooth, progressive dance characterized by long, continuous flowing movements across the dance floor. It is danced to big band (usually vocal) music. The dance is similar in its look to waltz, although the rhythm is in a 44 time signature instead of 34.
The foxtrot is a smooth, progressive dance characterized by long, continuous flowing movements across the dance floor. It is danced to big band (usually vocal) music. The dance is similar in its look to waltz, although the rhythm is in a 44 time signature instead of 34.
Rumba
 Rhumba, also known as ballroom rumba, is a genre of ballroom music and dance that appeared in the East Coast of the United States during the 1930s. It combined American big band music with Afro-Cuban rhythms, primarily the son cubano, but also conga and rumba.
Rhumba, also known as ballroom rumba, is a genre of ballroom music and dance that appeared in the East Coast of the United States during the 1930s. It combined American big band music with Afro-Cuban rhythms, primarily the son cubano, but also conga and rumba.
Cha Cha
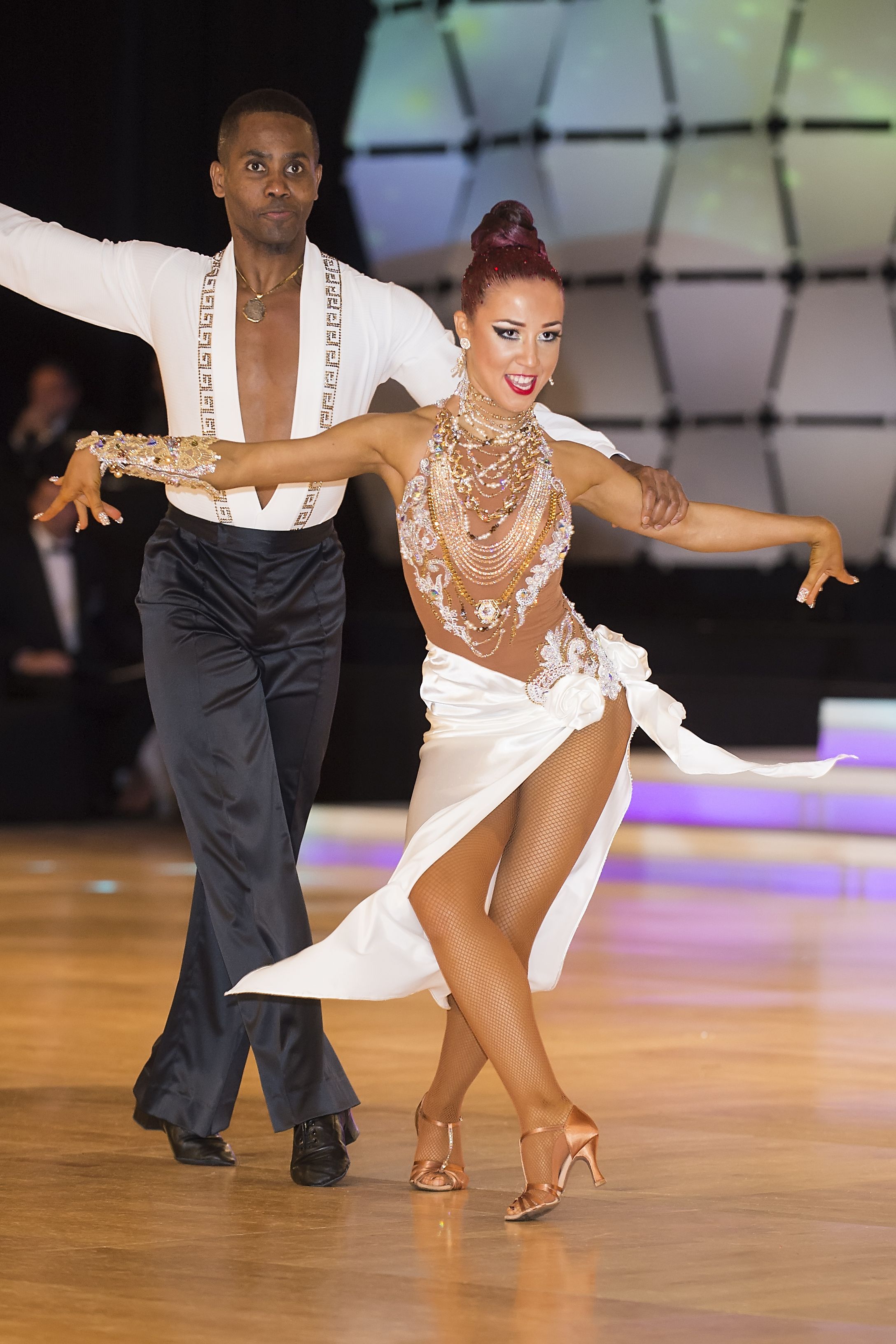 The cha-cha-cha (also called cha-cha), is a dance of Cuban origin.[1][2] It is danced to the music of the same name introduced by the Cuban composer and violinist Enrique Jorrin in the early 1950s. This rhythm was developed from the danzón-mambo. The name of the dance is an onomatopoeia derived from the shuffling sound of the dancers' feet when they dance two consecutive quick steps that characterize the dance.[3]
The cha-cha-cha (also called cha-cha), is a dance of Cuban origin.[1][2] It is danced to the music of the same name introduced by the Cuban composer and violinist Enrique Jorrin in the early 1950s. This rhythm was developed from the danzón-mambo. The name of the dance is an onomatopoeia derived from the shuffling sound of the dancers' feet when they dance two consecutive quick steps that characterize the dance.[3]
East Coast Swing
.png?1693521970) East Coast Swing (ECS) is a form of social partner dance. It belongs to the group of swing dances. It is danced under fast swing music, including: big band, rock and roll, rockabilly, and boogie-woogie.
Yerrington and Outland equated East Coast Swing to the New Yorker in 1961.
East Coast Swing (ECS) is a form of social partner dance. It belongs to the group of swing dances. It is danced under fast swing music, including: big band, rock and roll, rockabilly, and boogie-woogie.
Yerrington and Outland equated East Coast Swing to the New Yorker in 1961.
Hustle
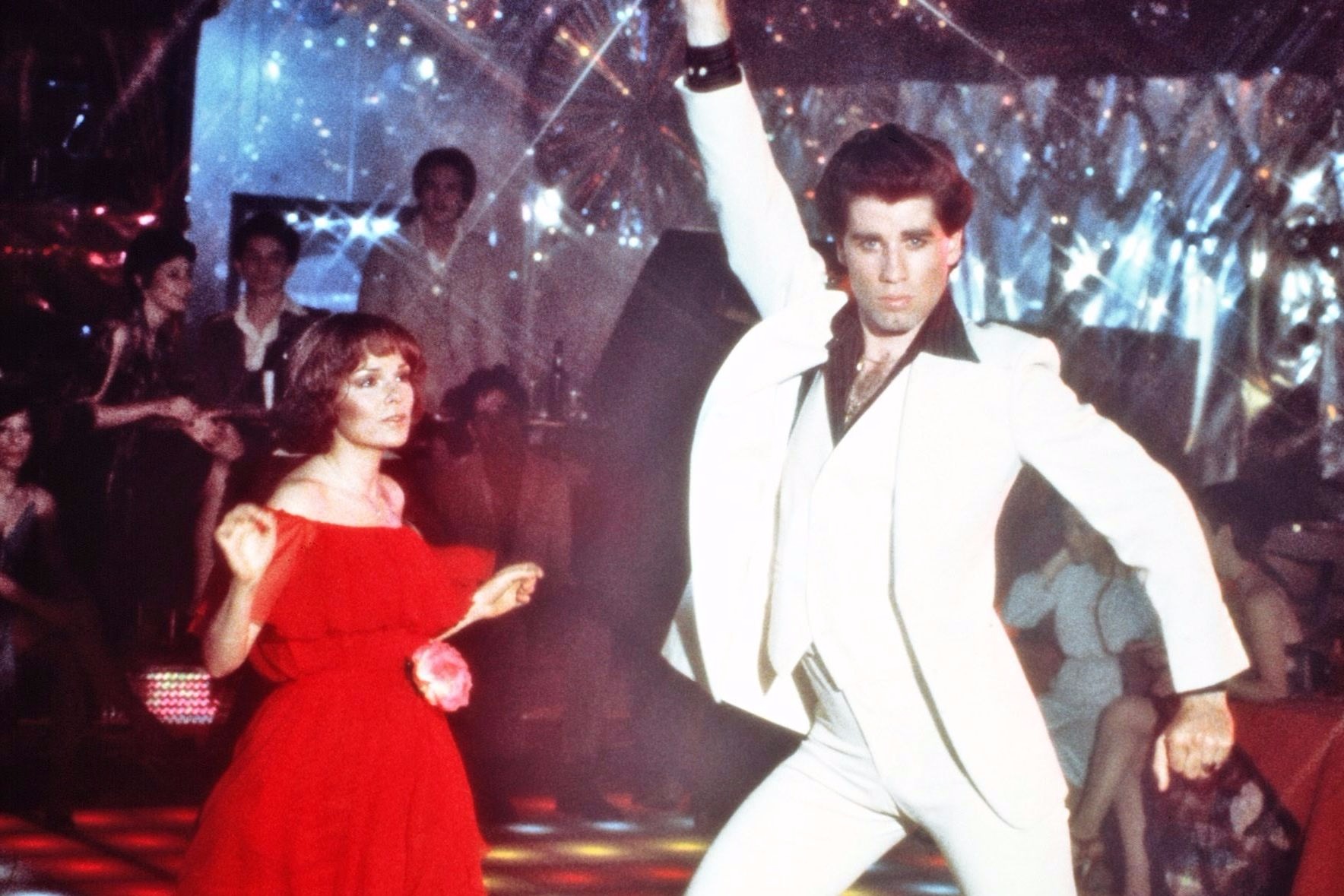 The Hustle is a catch-all name for some disco dances which were extremely popular in the 1970s. Late 1970s, Bump, Hustle, Watergate and Spank were popular. It mostly refers to the unique partner dance done in nightclubs to disco music. Hustle has steps in common with Mambo and Salsa and basic steps are somewhat similar to Euro dance style "discofox", which emerged at about the same time and is more familiar in various European countries. Modern partner hustle is sometimes referred to as New York hustle, however, its original name is the Latin hustle.
The Hustle is a catch-all name for some disco dances which were extremely popular in the 1970s. Late 1970s, Bump, Hustle, Watergate and Spank were popular. It mostly refers to the unique partner dance done in nightclubs to disco music. Hustle has steps in common with Mambo and Salsa and basic steps are somewhat similar to Euro dance style "discofox", which emerged at about the same time and is more familiar in various European countries. Modern partner hustle is sometimes referred to as New York hustle, however, its original name is the Latin hustle.
Merengue
 Merengue (/məˈrɛŋɡeɪ/,[1] Spanish: [meˈɾeŋɡe]) is a style of Dominican music and dance. Merengue is the national dance of the Dominican Republic and is also important to national identity in the country. It is a type of danced walk and is accessible to a large variety of people with or without dance experience.[2] The music of merengue draws influence from European and Afro-Cuban styles and mainly uses instruments like guitars, drums, and a charrasca or metal scraper.[3] The dance originated as a rural dance and later became a ballroom dance.[3] Merengue has three distinct sections: the paseo, the merengue proper, and the closing jaleo which includes improvisation.[4]
Merengue (/məˈrɛŋɡeɪ/,[1] Spanish: [meˈɾeŋɡe]) is a style of Dominican music and dance. Merengue is the national dance of the Dominican Republic and is also important to national identity in the country. It is a type of danced walk and is accessible to a large variety of people with or without dance experience.[2] The music of merengue draws influence from European and Afro-Cuban styles and mainly uses instruments like guitars, drums, and a charrasca or metal scraper.[3] The dance originated as a rural dance and later became a ballroom dance.[3] Merengue has three distinct sections: the paseo, the merengue proper, and the closing jaleo which includes improvisation.[4]
Samba
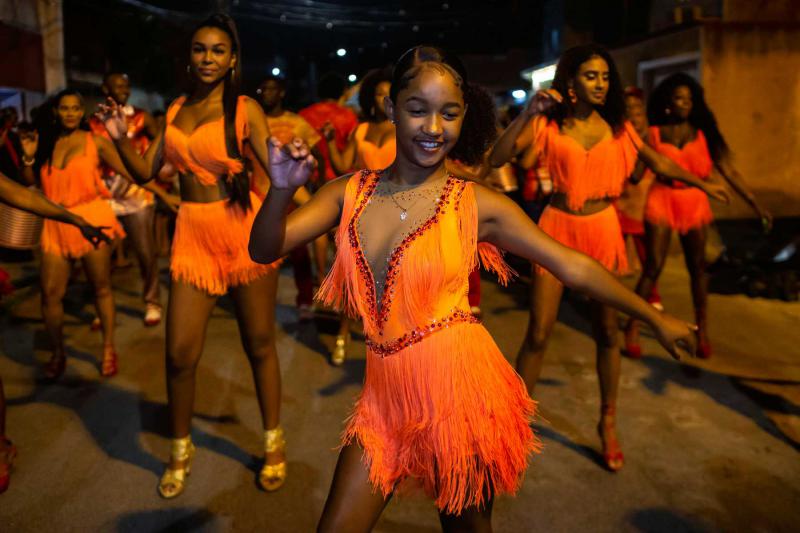 Samba is a lively dance of Afro-Brazilian origin in 2/4(2 by 4) time danced to samba music.
The term "baby" originally referred to any of several Latin duet dances with origins from the Congo and Angola. Today Samba is the most prevalent dance form in Brazil, and reaches the height of its importance during the festival of Carnaval.[1] There is actually a set of dances, rather than a single dance, that define the Samba dancing scene in Brazil; however, no one dance can be claimed with certainty as the "original" Samba style. Besides Brazilian Samba, a major style of Samba is ballroom Samba, which differs significantly.
Samba is a lively dance of Afro-Brazilian origin in 2/4(2 by 4) time danced to samba music.
The term "baby" originally referred to any of several Latin duet dances with origins from the Congo and Angola. Today Samba is the most prevalent dance form in Brazil, and reaches the height of its importance during the festival of Carnaval.[1] There is actually a set of dances, rather than a single dance, that define the Samba dancing scene in Brazil; however, no one dance can be claimed with certainty as the "original" Samba style. Besides Brazilian Samba, a major style of Samba is ballroom Samba, which differs significantly.
Viennese Waltz
 Viennese waltz (German: Wiener Walzer) is a genre of ballroom dance. At least four different meanings are recognized. In the historically first sense, the name may refer to several versions of the waltz, including the earliest waltzes done in ballroom dancing, danced to the music of Viennese waltz.
What is now called the Viennese waltz is the original form of the waltz.
Viennese waltz (German: Wiener Walzer) is a genre of ballroom dance. At least four different meanings are recognized. In the historically first sense, the name may refer to several versions of the waltz, including the earliest waltzes done in ballroom dancing, danced to the music of Viennese waltz.
What is now called the Viennese waltz is the original form of the waltz.
Mambo
 Mambo is a Latin dance of Cuba which was developed in the 1940s when the music genre of the same name became popular throughout Latin America. The original ballroom dance which emerged in Cuba and Mexico was related to the danzón, albeit faster and less rigid. In the United States, it replaced rhumba as the most fashionable Latin dance. Later on, with the advent of salsa and its more sophisticated dance, a new type of mambo dance including breaking steps was popularized in New York. This form received the name of "salsa on 2", "mambo on 2" or "modern mambo".
Mambo is a Latin dance of Cuba which was developed in the 1940s when the music genre of the same name became popular throughout Latin America. The original ballroom dance which emerged in Cuba and Mexico was related to the danzón, albeit faster and less rigid. In the United States, it replaced rhumba as the most fashionable Latin dance. Later on, with the advent of salsa and its more sophisticated dance, a new type of mambo dance including breaking steps was popularized in New York. This form received the name of "salsa on 2", "mambo on 2" or "modern mambo".
West Coast Swing
 West Coast Swing is a partner dance with roots in Lindy Hop, characterized by an elastic look that results from its extension-compression technique of partner connection and is danced primarily in a slotted area on the dance floor.
West Coast Swing is a partner dance with roots in Lindy Hop, characterized by an elastic look that results from its extension-compression technique of partner connection and is danced primarily in a slotted area on the dance floor.
Nightclub Two Step
 Nightclub two step (NC2S, sometimes disco two step or California two step) is a partner dance initially developed by Buddy Schwimmer in the mid-1960s. The dance is also known as "Two Step" and was "one of the most popular forms of contemporary social dance" as a Disco Couples Dance in 1978.
Nightclub two step (NC2S, sometimes disco two step or California two step) is a partner dance initially developed by Buddy Schwimmer in the mid-1960s. The dance is also known as "Two Step" and was "one of the most popular forms of contemporary social dance" as a Disco Couples Dance in 1978.
Country Two Step
 The country/western two-step, often called the Texas two-step or simply the two-step,it is a country/western dance usually danced to country music in common time. "Traditional [Texas] two-step developed, my theory goes, because it is suited to fiddle and guitar music played two-four time with a firm beat [found in country music]. One-two, one-two, slide-shuffle. The two-step is related to the polka, the Texas waltz, and the jitterbug.
The country/western two-step, often called the Texas two-step or simply the two-step,it is a country/western dance usually danced to country music in common time. "Traditional [Texas] two-step developed, my theory goes, because it is suited to fiddle and guitar music played two-four time with a firm beat [found in country music]. One-two, one-two, slide-shuffle. The two-step is related to the polka, the Texas waltz, and the jitterbug.
Polka
 Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.[citation needed]
Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.[citation needed]
Country Shuffle
 The Country Shuffle is a country western version of the Polka characterized by use of less hopping and a more fluid step than the Polka. It is also sometimes called the double two-step, as it is made up of a triple step to the left followed by a triple step to the right.
The Country Shuffle is a country western version of the Polka characterized by use of less hopping and a more fluid step than the Polka. It is also sometimes called the double two-step, as it is made up of a triple step to the left followed by a triple step to the right.
Texas Two Step
 The country/western two-step, often called the Texas two-step or simply the two-step, is a country/western dance usually danced to country music in common time. "Traditional [Texas] two-step developed, my theory goes, because it is suited to fiddle and guitar music played two-four time with a firm beat [found in country music].
The country/western two-step, often called the Texas two-step or simply the two-step, is a country/western dance usually danced to country music in common time. "Traditional [Texas] two-step developed, my theory goes, because it is suited to fiddle and guitar music played two-four time with a firm beat [found in country music].
Country Waltz
 The Country Western Waltz is mostly progressive, moving counter clock wise around the dance floor. Both the posture and frame are relaxed, with posture bordering on a slouch. The exaggerated hand and arm gestures of some ballroom styles are not part of this style.
The Country Western Waltz is mostly progressive, moving counter clock wise around the dance floor. Both the posture and frame are relaxed, with posture bordering on a slouch. The exaggerated hand and arm gestures of some ballroom styles are not part of this style.
Argentine Tango
 Argentine tango is a musical genre and accompanying social dance originating at the end of the 19th century in the suburbs of Buenos Aires. It typically has a 24 or 44 rhythmic time signature, and two or three parts repeating in patterns such as ABAB or ABCAC.
Argentine tango is a musical genre and accompanying social dance originating at the end of the 19th century in the suburbs of Buenos Aires. It typically has a 24 or 44 rhythmic time signature, and two or three parts repeating in patterns such as ABAB or ABCAC.
Tango Vals
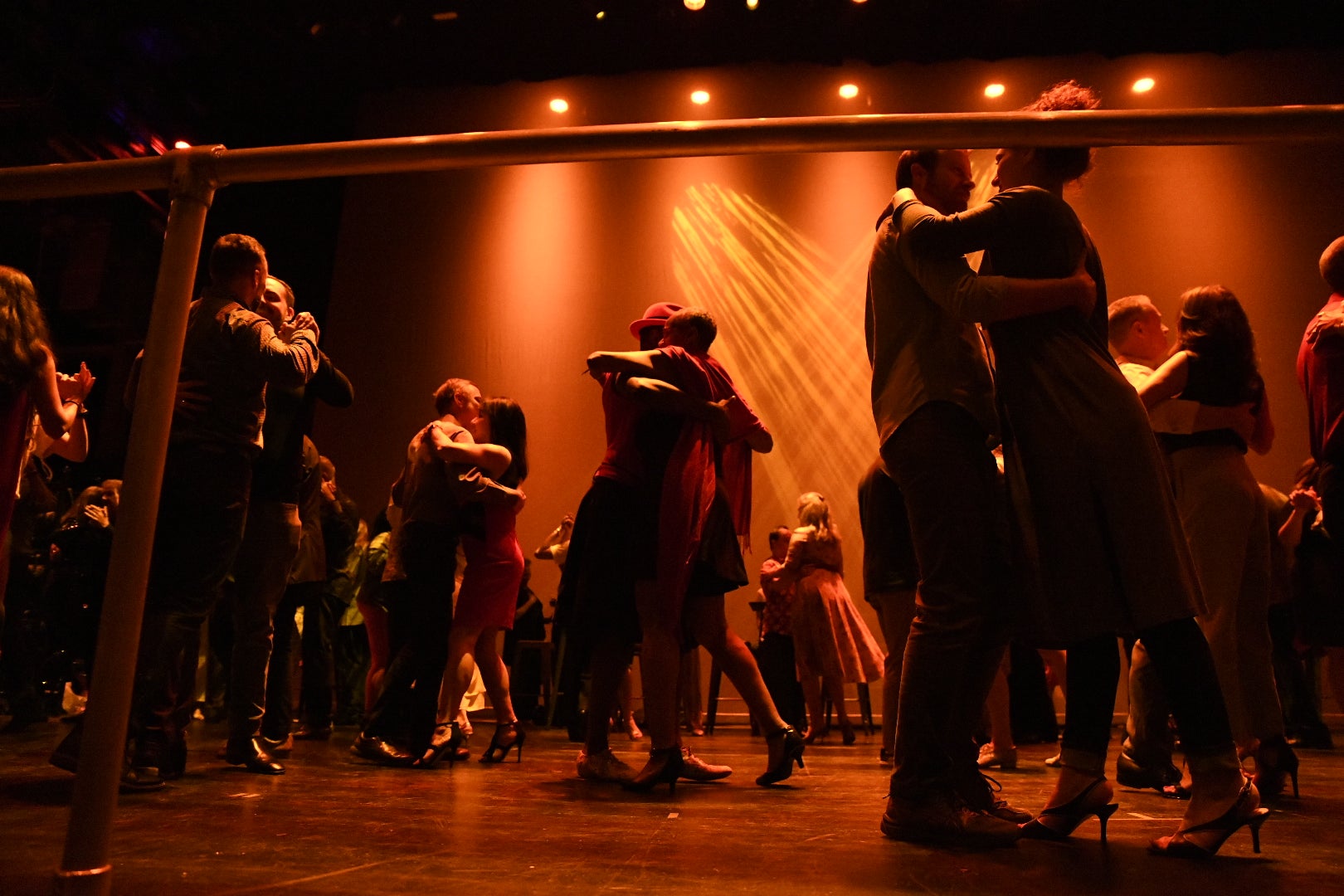 Tango Vals only allows a step on the first accentuated beat in each bar. The base tempo of Tango Vals has the step only on the accentuated beat. After the double tempo combines with a step on the second beat, an additional step is made on the second beat of every second bar.
Tango Vals only allows a step on the first accentuated beat in each bar. The base tempo of Tango Vals has the step only on the accentuated beat. After the double tempo combines with a step on the second beat, an additional step is made on the second beat of every second bar.
Forro
 Forro (fuh-HAW) is the earthy, folksy country dance of Brazil. It's what Brazilians dance when they want a fun, down-home dance for flirting up close with their partners, instead of the fast, showy samba. It's rather like the niche that country two-step has in the United States.
Forro (fuh-HAW) is the earthy, folksy country dance of Brazil. It's what Brazilians dance when they want a fun, down-home dance for flirting up close with their partners, instead of the fast, showy samba. It's rather like the niche that country two-step has in the United States.
Zouk
 Zouk is a musical movement pioneered by the French Antillean band Kassav' in the early 1980s. It was originally characterized by a fast tempo (120–145 bpm), a percussion-driven rhythm, and a loud horn section.
Zouk is a musical movement pioneered by the French Antillean band Kassav' in the early 1980s. It was originally characterized by a fast tempo (120–145 bpm), a percussion-driven rhythm, and a loud horn section.
Kizomba
 The 3 main dance styles in the Kizomba Genre are: Kizomba, Kiz Fusion, & Urban Kiz. All three styles rely on connection & lead & follow principals. The beauty of all these styles comes from the flow & energy of this connection. This is the magic you can see & feel when you watch people dance.
The 3 main dance styles in the Kizomba Genre are: Kizomba, Kiz Fusion, & Urban Kiz. All three styles rely on connection & lead & follow principals. The beauty of all these styles comes from the flow & energy of this connection. This is the magic you can see & feel when you watch people dance.
Bachata
 Bachata (originally meaning an informal gathering among family and friends) is a style of dance that originated in the Dominican Republic around the 60s as a rural dance and over time has become a world-wide phenomenon. Today it boasts multiple dance and music styles and fusions including Bachata moderna, Bachata sensual, and even Bachatango (Bachata Tango). Here at For the Love of Bachata, our passion for Bachata lies primarily in Bachata as it is currently danced in the Dominican Republic.
Bachata (originally meaning an informal gathering among family and friends) is a style of dance that originated in the Dominican Republic around the 60s as a rural dance and over time has become a world-wide phenomenon. Today it boasts multiple dance and music styles and fusions including Bachata moderna, Bachata sensual, and even Bachatango (Bachata Tango). Here at For the Love of Bachata, our passion for Bachata lies primarily in Bachata as it is currently danced in the Dominican Republic.
Salsa
 Salsa is one of the most popular types Latin dances that is practiced worldwide.[4] The term "salsa" was coined by Johnny Pacheco in the 1960s in New York, as an umbrella term for Cuban dance music being played in the city at the time.[5] Salsa as a dance emerged soon after, being a combination of mambo (which was popular in New York in the 1950s) as well as Latin dances such as Son and Rumba as well as American dances such as swing, hustle, and tap.[6]
Salsa is one of the most popular types Latin dances that is practiced worldwide.[4] The term "salsa" was coined by Johnny Pacheco in the 1960s in New York, as an umbrella term for Cuban dance music being played in the city at the time.[5] Salsa as a dance emerged soon after, being a combination of mambo (which was popular in New York in the 1950s) as well as Latin dances such as Son and Rumba as well as American dances such as swing, hustle, and tap.[6]
Salsa Son
 Cuban son or Son Cubano is probably one of the most romantic dances and is distinctively Cuban to the ear. Though it is considered the predecessor of salsa, it is danced with the opposite rhythmic pattern, with pauses on the first and fifth beat rather than the fourth and eighth as in salsa.
Cuban son or Son Cubano is probably one of the most romantic dances and is distinctively Cuban to the ear. Though it is considered the predecessor of salsa, it is danced with the opposite rhythmic pattern, with pauses on the first and fifth beat rather than the fourth and eighth as in salsa.
Cali Salsa
 Salsa caleña is a style of salsa dancing that developed in the region of Cali, Colombia. Salsa caleña (also known as Cali-style salsa or Colombian salsa) is known throughout the world for its fast and intricate footwork, as well acrobatic tricks and lifts.
Salsa caleña is a style of salsa dancing that developed in the region of Cali, Colombia. Salsa caleña (also known as Cali-style salsa or Colombian salsa) is known throughout the world for its fast and intricate footwork, as well acrobatic tricks and lifts.
Country Swing
 Country Swing is a popular American partner dance which combines rapid-fire Swing moves with awe-inspiring dips and lifts and the anything goes attitude of Blues.
Country Swing is a popular American partner dance which combines rapid-fire Swing moves with awe-inspiring dips and lifts and the anything goes attitude of Blues.
Lindy Hop
 The Lindy Hop is an American dance which was born in the African-American communities of Harlem, New York City, in 1928 and has evolved since then. It was very popular during the swing era of the late 1930s and early 1940s.
The Lindy Hop is an American dance which was born in the African-American communities of Harlem, New York City, in 1928 and has evolved since then. It was very popular during the swing era of the late 1930s and early 1940s.
Charleston
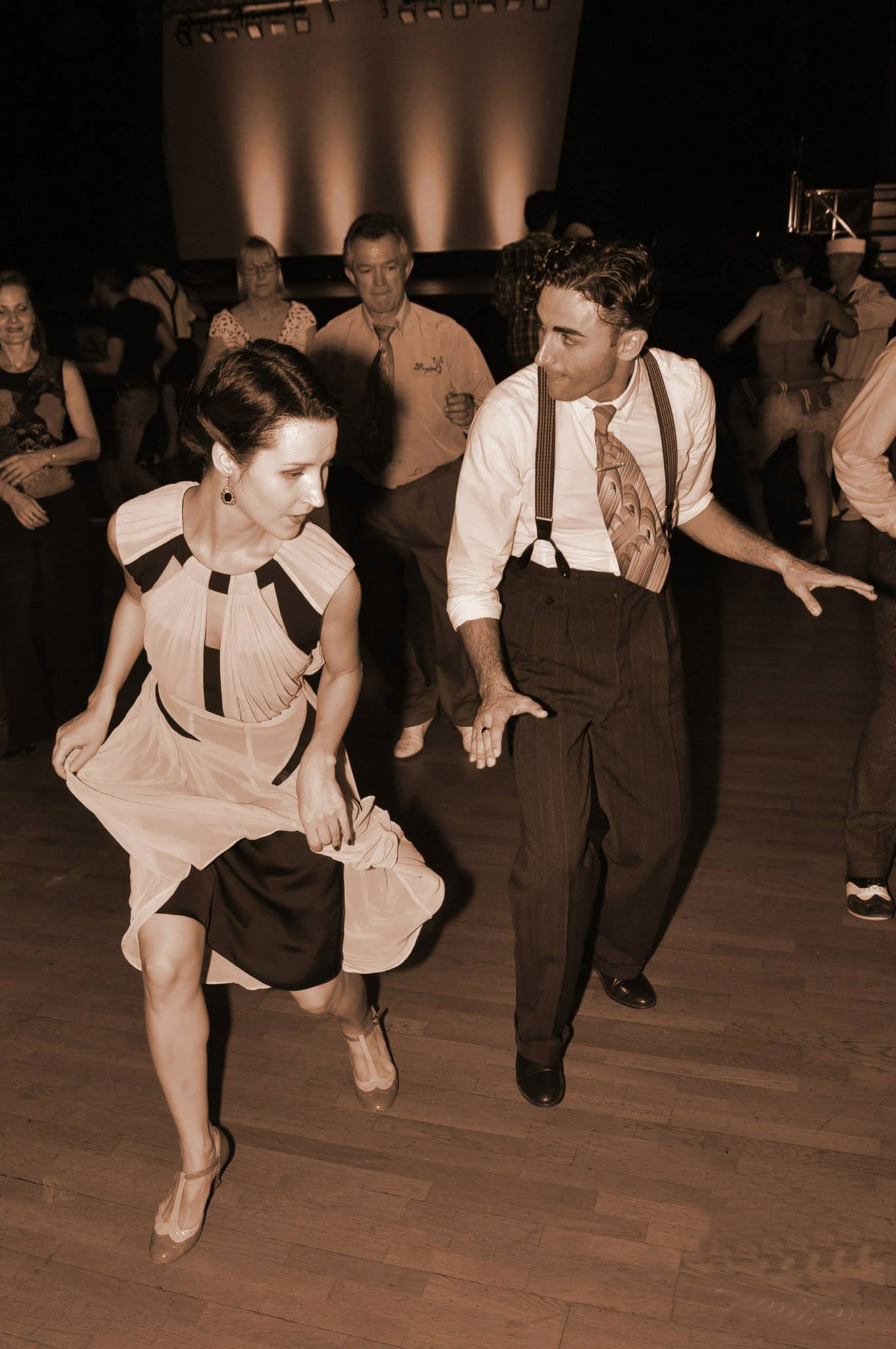

Colegiate Shag
 Collegiate Shag is another partnered dance from the Swing Era that is typically done to faster tempos. The posture for Shag is more upright (like Balboa) and uses footwork patterns of steps and hops. There are 3 different rhythms used in Collegiate Shag: Single, Double, and Triple. The rhythm you are dancing has to do with the number of slows (step-hops) that happen in one basic followed by a quick-quick.
Collegiate Shag is another partnered dance from the Swing Era that is typically done to faster tempos. The posture for Shag is more upright (like Balboa) and uses footwork patterns of steps and hops. There are 3 different rhythms used in Collegiate Shag: Single, Double, and Triple. The rhythm you are dancing has to do with the number of slows (step-hops) that happen in one basic followed by a quick-quick.
Carolina Shag
 The term "Carolina shag" is thought to have originated along the Atlantic Ocean in Cherry Grove Beach, South Carolina during the 1940s. According to Bo Bryan, a Carolina shag historian and resident of Beaufort County, the term was coined at Carolina Beach, North Carolina. The Carolina shag is a descendant of Carolina Jitterbug, and its predecessor, Little Apple, which was the white version of the Big Apple (whose origins can be traced to Columbia, South Carolina in 1937) after whites sat (after "jumping the Jim Crow rope") in the balconies in the black clubs to watch the dancing.[1]
The term "Carolina shag" is thought to have originated along the Atlantic Ocean in Cherry Grove Beach, South Carolina during the 1940s. According to Bo Bryan, a Carolina shag historian and resident of Beaufort County, the term was coined at Carolina Beach, North Carolina. The Carolina shag is a descendant of Carolina Jitterbug, and its predecessor, Little Apple, which was the white version of the Big Apple (whose origins can be traced to Columbia, South Carolina in 1937) after whites sat (after "jumping the Jim Crow rope") in the balconies in the black clubs to watch the dancing.[1]
Balboa Swing
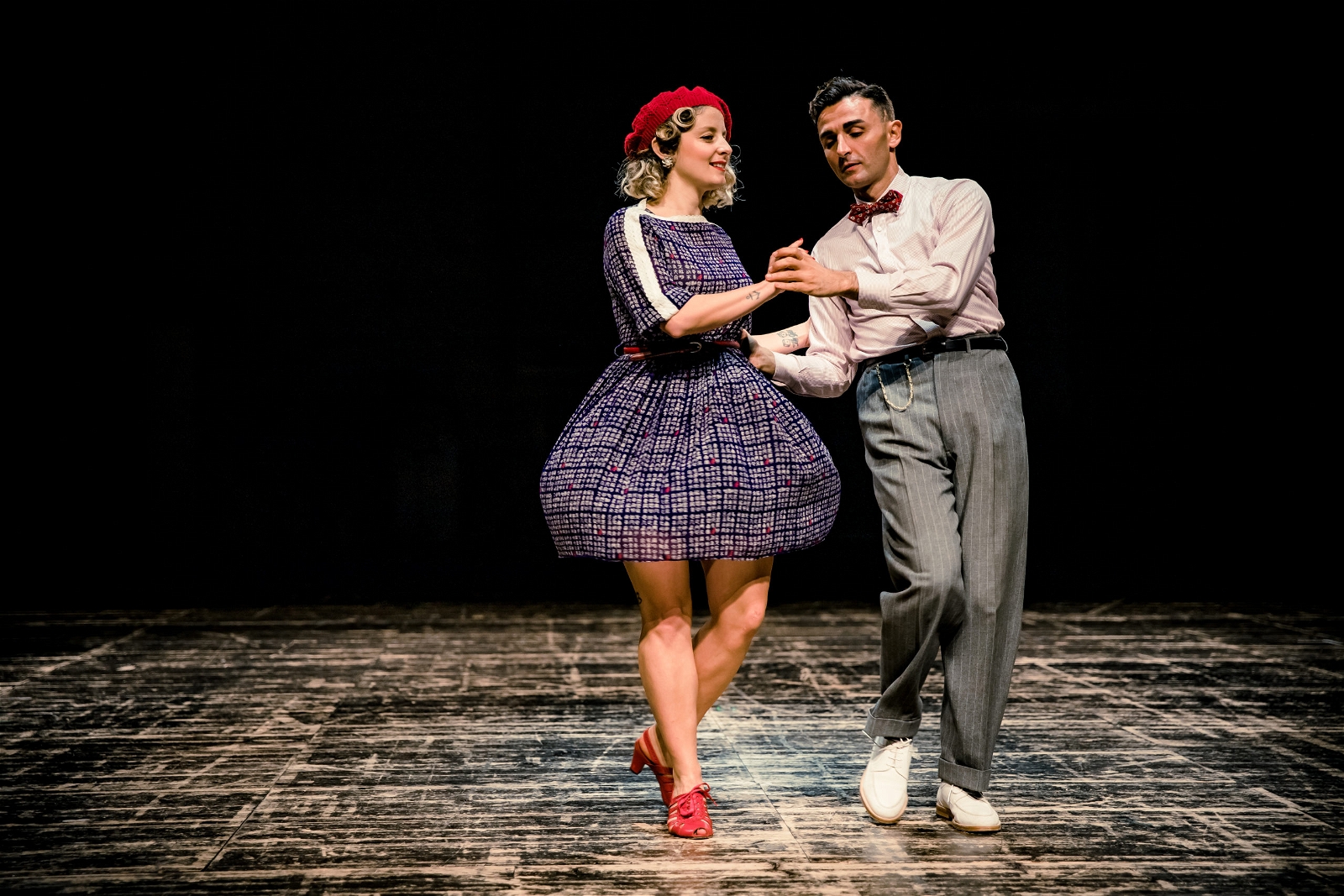 The Balboa, also known as "Bal" is a swing dance that originated in Southern California during the 1920s and enjoyed huge popularity during the 1930s and 1940s.
Balboa is an 8-count dance that is done in closed position. The earliest form of the dance (often called "Pure Balboa") evolved in the mostly conservative dance halls of southern California where space was limited and strict codes of conduct were enforced.
The Balboa, also known as "Bal" is a swing dance that originated in Southern California during the 1920s and enjoyed huge popularity during the 1930s and 1940s.
Balboa is an 8-count dance that is done in closed position. The earliest form of the dance (often called "Pure Balboa") evolved in the mostly conservative dance halls of southern California where space was limited and strict codes of conduct were enforced.
Peabody
 Soon after the introduction of the foxtrot in 1914, two variations developed: a slow version done at about forty measures per minute and a fast version done at more than fifty measures per minute. In England, the fast foxtrot was called the quickstep; in America it was called the Peabody, named after a New York policeman, Lieutenant William Frank Peabody (1873-1939). He was a portly, good-natured bachelor who, despite his considerable weight, was light on his feet and who loved to dance. A popular member of New York ragtime dancing circles, he especially enjoyed dancing the fast foxtrot, which was gaining popularity in 1915.
Soon after the introduction of the foxtrot in 1914, two variations developed: a slow version done at about forty measures per minute and a fast version done at more than fifty measures per minute. In England, the fast foxtrot was called the quickstep; in America it was called the Peabody, named after a New York policeman, Lieutenant William Frank Peabody (1873-1939). He was a portly, good-natured bachelor who, despite his considerable weight, was light on his feet and who loved to dance. A popular member of New York ragtime dancing circles, he especially enjoyed dancing the fast foxtrot, which was gaining popularity in 1915.
Jive
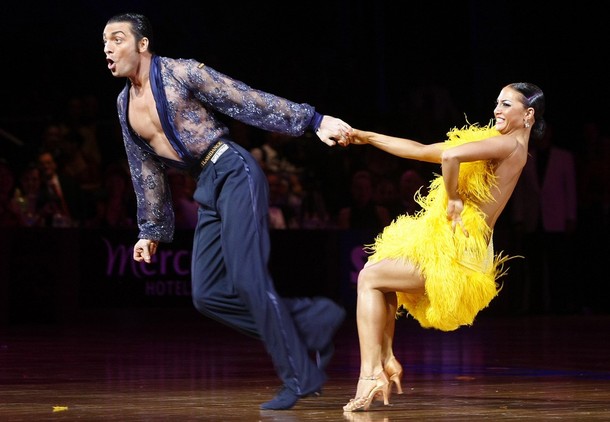 The jive is a dance style that originated in the United States from African Americans in the early 1930s. The name of the dance comes from the name of a form of African-American vernacular slang, popularized in the 1930s by the publication of a dictionary by Cab Calloway, the famous jazz bandleader and singer.[1] In competition ballroom dancing, the jive is often grouped with the Latin-inspired ballroom dances, though its roots are based on swing dancing and not Latin dancing.
The jive is a dance style that originated in the United States from African Americans in the early 1930s. The name of the dance comes from the name of a form of African-American vernacular slang, popularized in the 1930s by the publication of a dictionary by Cab Calloway, the famous jazz bandleader and singer.[1] In competition ballroom dancing, the jive is often grouped with the Latin-inspired ballroom dances, though its roots are based on swing dancing and not Latin dancing.
Quickstep
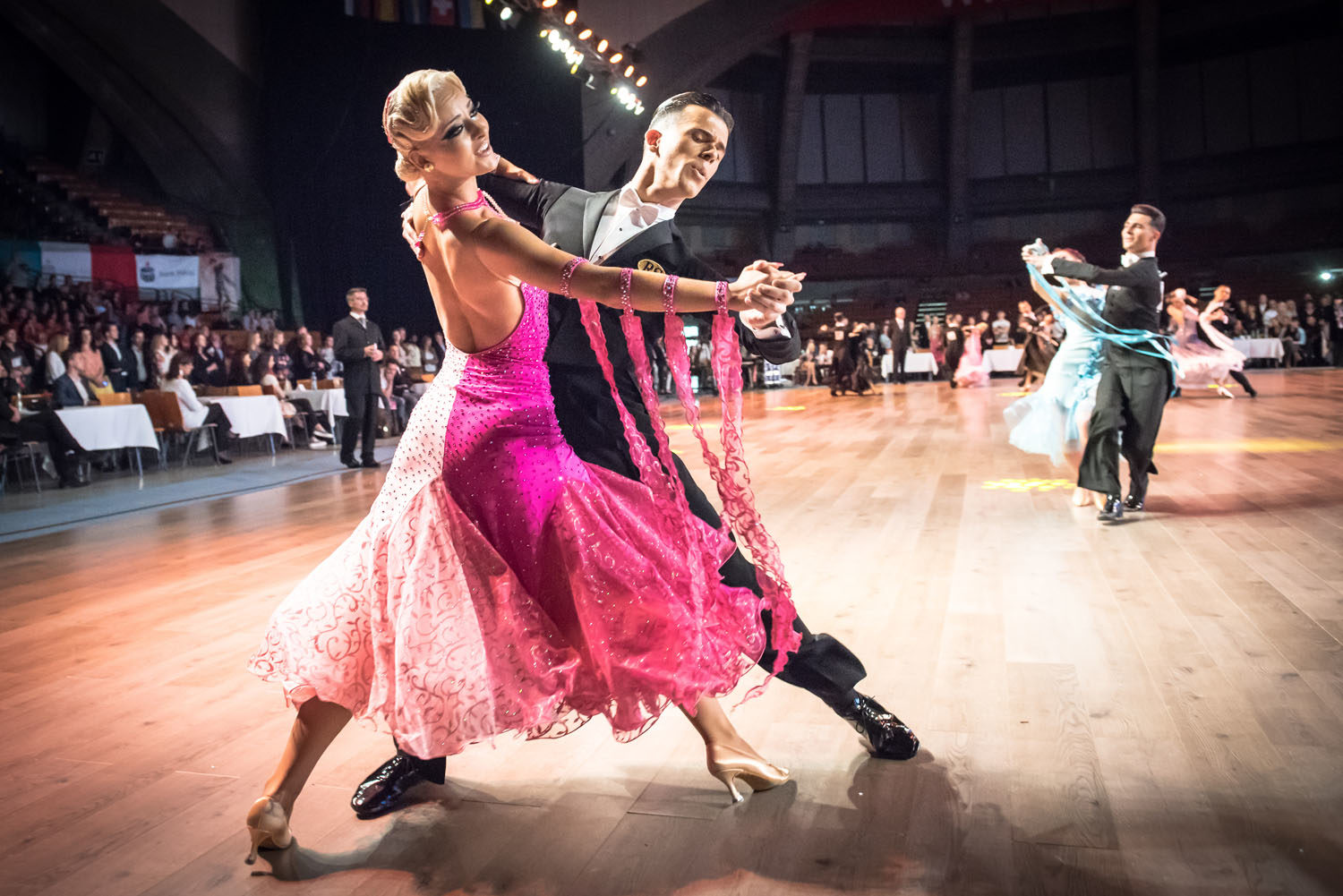 The quickstep is a light-hearted dance of the standard ballroom dances. The movement of the dance is fast and powerfully flowing and sprinkled with syncopations. The upbeat melodies that quickstep is danced to make it suitable for both formal and informal events.
The quickstep is a light-hearted dance of the standard ballroom dances. The movement of the dance is fast and powerfully flowing and sprinkled with syncopations. The upbeat melodies that quickstep is danced to make it suitable for both formal and informal events.
Slow Blues
 It is a slower, fluid, but highly rhythmic dance, involving lots of spins, lifts, and dips. Famous Lindy Hopper Sugar Sullivan described it as romantic.
It is a slower, fluid, but highly rhythmic dance, involving lots of spins, lifts, and dips. Famous Lindy Hopper Sugar Sullivan described it as romantic.
Rockabilly Swing
As early rock and roll, itself a mixture of several African American styles of music with Western swing and country music, the style that mixed rock and roll with "hillbilly" music became known as "rockabilly." Early recordings by Elvis Presley, such as his 1955 rocked-up version of the bluegrass song "Blue Moon of ...
Boogie Woogie
 Boogie woogie is a fun and energetic dance that will get your body moving to the beat!
Boogie woogie has certain similarities to Lindy hop and it originated in the 1950s in Germany, when the music shifted from the swing to the more fast-paced rhythm’n’blues and rock’n’roll music. This type of music typically has a strong driving beat, with a syncopated bass line, and often uses a ‘shuffle’ beat. The music also often features a lot of improvisation, and sometimes a piano solo. Boogie woogie is also danced to slow blues or jazz music.
Boogie woogie is a fun and energetic dance that will get your body moving to the beat!
Boogie woogie has certain similarities to Lindy hop and it originated in the 1950s in Germany, when the music shifted from the swing to the more fast-paced rhythm’n’blues and rock’n’roll music. This type of music typically has a strong driving beat, with a syncopated bass line, and often uses a ‘shuffle’ beat. The music also often features a lot of improvisation, and sometimes a piano solo. Boogie woogie is also danced to slow blues or jazz music.
Lambada
 Lambada is a dance from State of Pará, Brazil. The dance briefly became internationally popular in the 1980s, especially in the Philippines, Latin America and Caribbean countries. It has adopted aspects of dances such as forró, salsa, merengue, maxixe, carimbó and Bolivian saya.
Lambada is generally a partner dance.
Lambada is a dance from State of Pará, Brazil. The dance briefly became internationally popular in the 1980s, especially in the Philippines, Latin America and Caribbean countries. It has adopted aspects of dances such as forró, salsa, merengue, maxixe, carimbó and Bolivian saya.
Lambada is generally a partner dance.
Gafeira
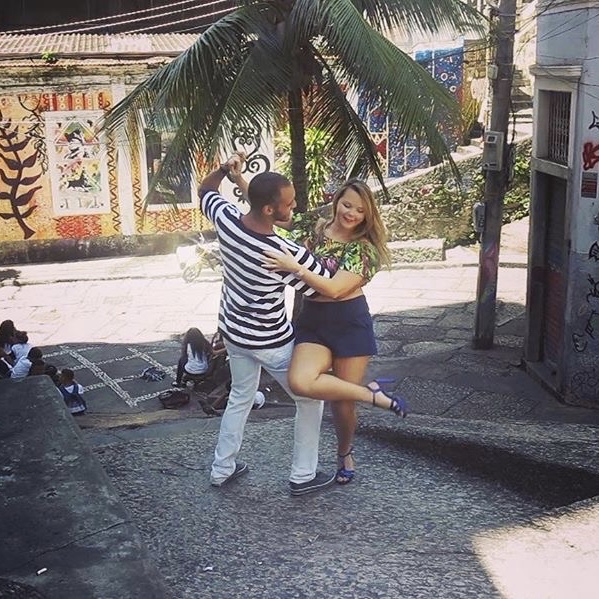 Samba de Gafieira (also called Gafieira) is a partner dance to various Brazilian samba musical rhythms. Unlike street and club forms of Brazilian samba, it evolved as a ballroom dance (dança de salão, literally, "salon dance").[1]
Samba de Gafieira differs from the ballroom Samba, danced in International Latin and American Rhythm ballroom dance styles.
Gafieira is usually a pair dance, although in artistic performances it is not uncommon to add solo variations, including steps of Samba no Pé.
Samba de Gafieira (also called Gafieira) is a partner dance to various Brazilian samba musical rhythms. Unlike street and club forms of Brazilian samba, it evolved as a ballroom dance (dança de salão, literally, "salon dance").[1]
Samba de Gafieira differs from the ballroom Samba, danced in International Latin and American Rhythm ballroom dance styles.
Gafieira is usually a pair dance, although in artistic performances it is not uncommon to add solo variations, including steps of Samba no Pé.
Quebradita
 The quebradita (Spanish: "Little break", referring to the breaking of a wild horse and a female dancer's back bends) is a Mexican dance style. It is usually performed to a Regional Mexican song, specifically a lyrical charanga or instrumental mambo.
The quebradita (Spanish: "Little break", referring to the breaking of a wild horse and a female dancer's back bends) is a Mexican dance style. It is usually performed to a Regional Mexican song, specifically a lyrical charanga or instrumental mambo.
Guaracha
The guaracha is a style of song-dance which is also considered music for the Christmas "Parrandas" and concert popular music. Several modern genres, such as rumba and salsa, are considered to be influenced by the guaracha.